The future for bulk handling is preventive and predictive maintenance

Effective upkeep of high-tonnage conveyor systems is critical to maintaining production and profitability, and maintenance repair and operations (MRO) professionals need a comprehensive plan with a foundation built on workplace safety. Formulating such a strategy requires an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of reactive maintenance (RM), preventive maintenance (PM), and predictive maintenance (PdM), with goals that include minimizing unscheduled downtime, improving safety, raising efficiency, and reducing the overall cost of operation to achieve a better return on investment (ROI).
Reactive maintenance
Even today, many companies practice what can be called reactive maintenance on their conveyors, meaning they simply fix whatever breaks. Components are left to run until they fail, and the resulting system downtime is unscheduled, disruptive, and expensive. Among the contributors to the costs of this approach are unplanned production stoppages, ancillary equipment damage (when a broken component damages something else), overtime, and emergency service fees.
Other disadvantages include shorter asset life expectancy, since components are not maintained in optimal running condition, as well as uncontrolled budgets and potential safety hazards. Further, technicians tend to take more risks and make more mistakes when under pressure to restore operation in the shortest possible time frame.

Despite the clear downside of a predominantly reactive maintenance strategy, it has been estimated that half of all the conveyor maintenance activities in the average North American facility follow this approach. The obvious reason is budget: reactive maintenance requires less staff, less planning, and a lower initial investment. But such a strategy leads to ineffective planning, insufficient oversight, and far less system control.
The shift to preventive maintenance
The deficiencies of reactive maintenance have driven an evolution to a more preventive approach to minimize failures that force unplanned shutdowns for repairs. Guidelines are typically based on time in service or operating hours. The idea of PM has been around almost since the invention of the wheel: performing regular maintenance on equipment to reduce the chances of failure. It is the same approach that consumers use when they take their car in for scheduled oil changes to extend engine life.
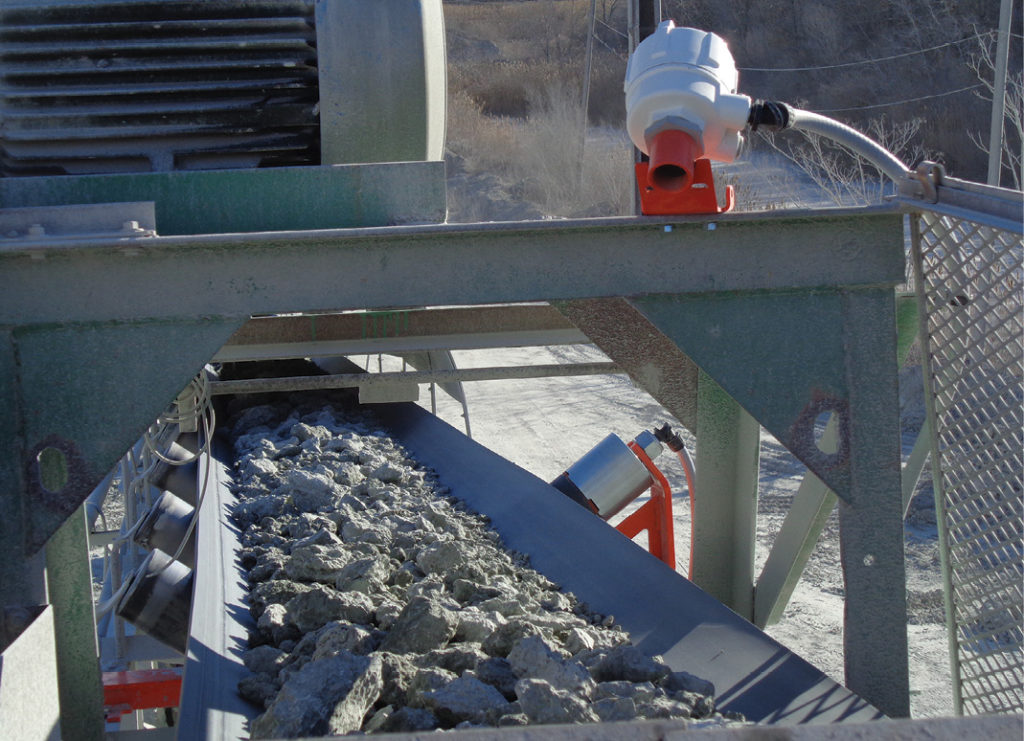

Bulk handling equipment endures ongoing punishment by transporting millions of tons of rock, aggregate, and sand in fluctuating weather conditions, potentially creating dust emissions, spillage, and carryback. PM prolongs component life, increases productivity, improves overall efficiency, and reduces maintenance costs. Also, an effective PM schedule requires strict adherence and consistent updating.
Some firms take this responsibility in-house, but others find that specialist service providers deliver a better return on their maintenance investment, relying on the expertise and scheduled maintenance from industry experts so their employees can focus on core activities.
Generally triggered by time, metered inspection or common indicators (mistracking, spillage, etc.), the PM approach to conveyor maintenance assumes that each component has a typical equipment life based upon previous similar applications and environments. Using observation and experience, PM determines when relevant parts should be retired, replaced, or refurbished, before the expected failure point. The result is generally greater safety, higher system efficiency, reduced spillage, and better overall system control.
The cost of preventive maintenance
Equipment life estimates often do not account for performance in varying service conditions, so calculating cost projections based on the rate of failure drawn from data of similar applications remains largely theoretical. In most situations, PM can be no more than an educated guess, allowing for the conditions, application, and operating schedule (among several other variables). However, a primary issue with PM is that some parts will inevitably be serviced too frequently, driving up costs, while others will not be serviced often enough, leading to degraded performance at best and catastrophic failures at worst.
Maintenance on bulk handling systems also depends on the availability of parts, age of equipment, trained labor to perform the work, and the regulations around each procedure. Operations such as coal-fired boilers, cement production, and smelting plants may require cool-down and ramp-up periods that can take days on either end of the maintenance work and introduce added safety concerns (personal protective equipment, confined space entry, exposure limits, etc.).
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance (PdM) directly monitors equipment performance during normal operation to more accurately anticipate failure. Relying on sensors and supported by software, it collects information over time, aggregates the facts and uses an algorithm to deliver a practical result that is made available to stakeholders. When combined with regular physical inspections, this type of data-driven system provides far more complete, accurate, and actionable information for service technicians and operations personnel.
Some component manufacturers offer structured conveyor inspections and belt cleaner maintenance as part of a managed service relationship. Their monitoring systems can track component wear and update the service technician and/or operations team via wifi or cell phone on upcoming service needs. The technology will also send an alert through a mobile app in the event of upset conditions, allowing service technicians and plant operators to access real-time data. There are some new systems that can even adjust belt cleaner tension automatically.
Highly trained service technicians provide an added set of eyes on the conveyors, travelling to and from the equipment to be serviced and logging details in their reports. Because they see so many different applications, they can often alert on problems that general maintenance personnel overlook or have become accustomed to ignoring. With factory-direct managed service, the responsibility for maintenance falls on the provider, allowing the staff to focus on other priorities.
Unlike PM that is determined by an average or expected life statistic, PdM is based on the actual condition of the equipment. Sometimes called “condition-based maintenance,” when predictive analysis identifies a potential issue, the repair can be scheduled at a time that minimizes the impact on production. The benefits include further optimized system performance and component life, reducing the need for visual inspection, and minimizing guesswork through a more automated, analytics-based system. Although it does not fully eliminate the need for personal inspections and maintenance, for conveyor systems that can be miles long and, in some cases, cover difficult terrain, this approach saves time and reduces potential hazards.
Predictive maintenance implementation
A predictive maintenance program starts with data collection and storage, and then proceeds to analysis. In the past, adding new points of measurement was a time-consuming and expensive undertaking, but wireless instruments have greatly reduced these costs. With more readily available data collection, storage and analytics options, some bulk material handlers are recognizing that each critical component can and should be monitored and analyzed to optimize performance. Sensors can also feed data to cloud-based software which then broadcasts it to the mobile apps in the field.
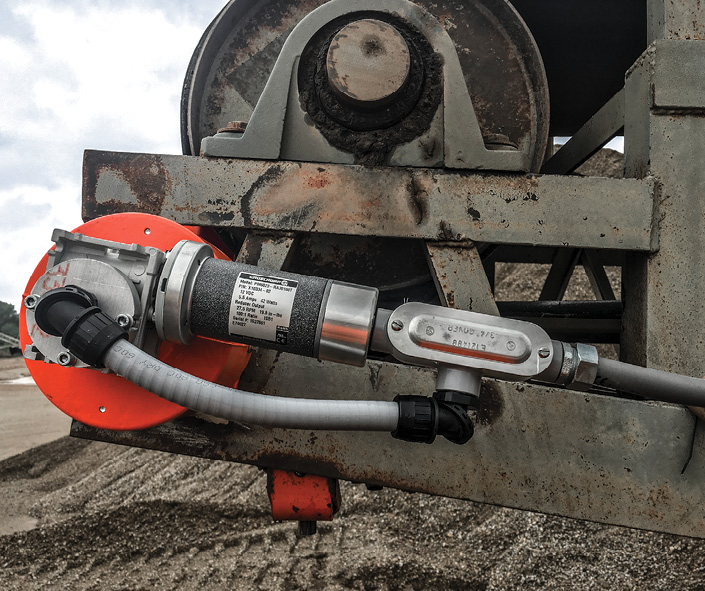

The initial capital expenditure for these systems may appear steep, but cloud-based technology can defray some of the entry cost. The benefits of extended equipment life, tighter budget forecasting, more reliable maintenance scheduling, increased worker efficiency, decreased downtime, and better productivity all add to a swift ROI.
Machine learning
Unlike PM, which relies on wear life determined by manufacturer and/or operator observations, machine learning adapts maintenance needs to the operation and service environment, fueled by all previous input. The benefit is a tailored experience that has the effect of equipment seeming to communicate its needs directly to decision makers.
A recently commercialized example is a belt cleaner position indicator that monitors the blade, tracking and reporting its remaining service life. The intuitive device continuously gathers data on primary belt cleaners, notifying factory-trained service technicians and/or plant operations personnel when re-tensioning or replacement is required or when abnormal conditions occur. Managers and service technicians can quickly access info on any networked cleaner via cell phone or Wi-Fi.
The device delivers critical real-time intelligence and reduces worker exposure to moving conveyors, improving both efficiency and safety. Maintenance planning is simplified by having detailed information available on demand, allowing service personnel to deliver and install replacement wear parts during scheduled outages. Relying on actual operating conditions instead of human judgement to monitor blade wear and tension for optimal cleaning performance, the indicator maximizes the blade’s usable surface area and reports with certainty when a blade is nearing the end of its useful life.
Taking the technology a step further is a patent-pending device that combines the position indicator with an automated belt cleaner tensioner. This novel powered assembly incorporates sensors that constantly monitor blade pressure and adjust its position to maintain optimal cleaning tension. Maintenance personnel no longer need to visit each cleaner and manually re-tension. Instead, the tasks are performed automatically, reducing maintenance time while maximizing the usable area of every cleaner. This takes the concept of preventive maintenance to another level: rather than optimize for a process parameter or other metric, the approach makes real-time profitability the priority outcome.
Combining the power of PM and PdM
Predictive maintenance has many advantages over preventive maintenance, but in the past, it was often too expensive or impractical to implement this strategy on all but the most critical components. Now that data collection, storage, and analysis are becoming easier and less expensive, additional components and systems are likely to become part of a plant’s conveyor maintenance program.
Bulk material handling systems working in harsh operating environments experience unexpected failure events that can be difficult to predict when they are caused by random, abnormal overloads or human error. So, maintenance staff need to have some capacity to react to sudden failures. During unscheduled downtime, managed service providers can take advantage of the outage to maintain or upgrade equipment.
Some service providers are also taking steps to help customers whose facilities have limited access during the Covid-19 pandemic by training maintenance staff remotely to effectively maintain their conveyor systems, offering guidelines on preventive maintenance, inspections, and replacement blade options. Factory-direct technicians remain in close contact with periodic check-ins and operate within key parameters to assure optimum performance.
With the goal of an efficient and cost-effective maintenance schedule, human labor will always be needed to design and carry out solutions, just like data will always rely on human experience to be properly applied. That is why leveraging the benefits of both PM and PdM is the best approach. Because unscheduled downtime, prematurely degraded wear parts, and unnecessary labor have such a serious impact on the cost of operation, applying both methods to a maintenance strategy maximizes the effectiveness of both.
Daniel Marshall is a product engineer, Martin Engineering.
Comments
Emmanuel Adu Nyinaku
Well explained